In this post I would like to describe a simple technique for reducing the waiting time and stress related to build agent environment volatility when using Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery tools like GoCD, via infrastructure testing.
The Problem
Given a modern CI server, such as GoCD, and a set of dedicated build machines (agents), it is possible to improve software development agility. Automated build/test/deploy pipelines, built to reflect the value stream, bring transparency and focus into the software delivery activities.
CI automation is software itself, and is thus susceptible to errors. Configuration management can optimize the set up of the environment, in which the build agents run. However, when computational resources are added to a CI infrastructure, i.e. to parallelize the build and thus reduce feedback times, a missing environment dependency can cause stress and pain that CI is trying to eliminate.
Consider a pipeline where a complete cycle (i.e. with slow integration tests followed by a reporting step at the end or long check-outs in the beginning) takes a significant amount of time. If one of the last tasks fails due to a configuration or an environment issue, the whole stage fails. The computational resources have been wasted just to find out that a compiler is missing. This can easily happen when there is variation in the capabilities of the build agents.
Improvement idea: fail fast! Don’t wait for environment or infrastructure mismatches
GoCD Resources as Requirements and Capabilities
If a step in a build pipeline requires a certain compiler or a particular environment, this can be conveniently expressed in the configuration of GoCD as a build agent resource. A resource can be seen as a requirement of a pipeline step that is fulfilled by a corresponding capability of a build agent.
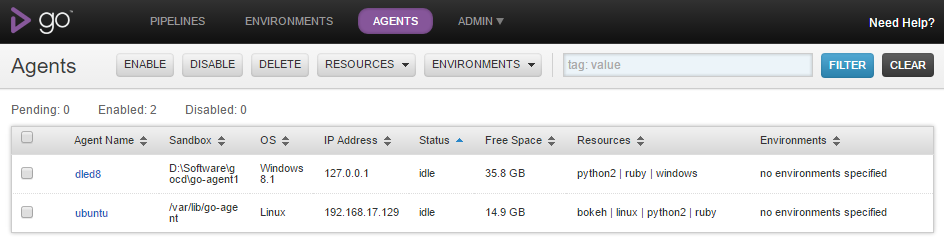
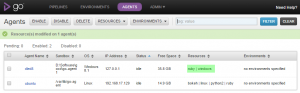
Consider the following set-up with two build agents – one running on Windows, another one on Linux. Some tasks could be completely platform-independent, such as text processing, and thus could be potentially performed on any machine with a required interpreter installed.
Build Agent is the Culprit
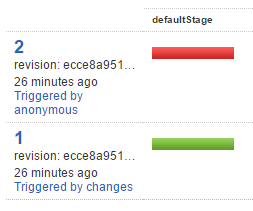
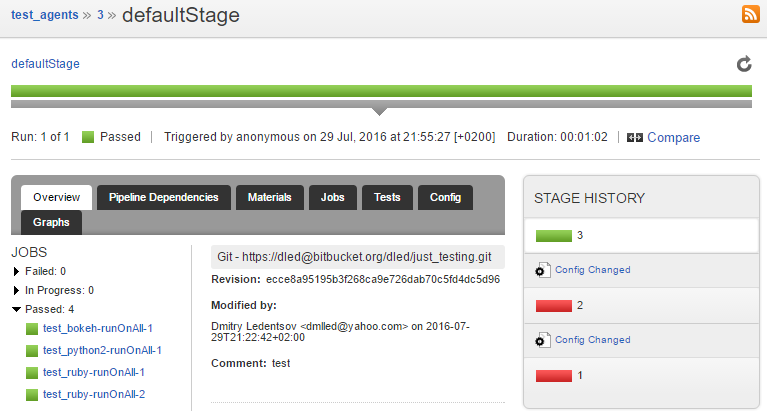
We have set up our environment, and have successfully tested our first commit, but the second one fails:
The code is the same, why did the second build fail? The builds ran on different agents, but I expected them to behave similarly…
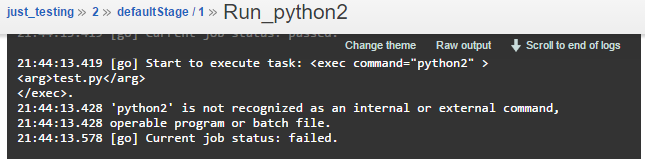
Oh, that’s embarrassing. While yes, the script is platform-independent, there’s no executable named python2 in my Windows runner environment path.
With a one-file repository and a simple print statement this failure did not cause much damage, but as mentioned earlier, real life builds failing due to a missing executable might be costly.
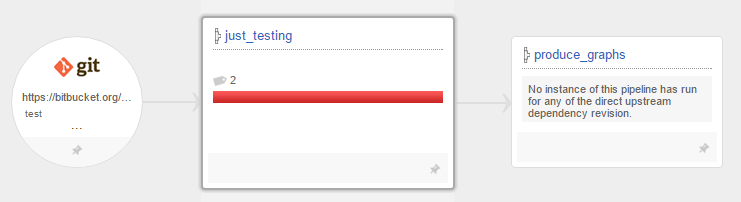
Unhappy Picture
Infrastructure Test Pipeline
In order to fail fast in situations where new agents are added to a CI infrastructure, or their environment is volatile, I propose to use a single independent pipeline that checks the assumptions that longer builds depend upon.
If a build step requires python in the path, there should be a test for it that gives this feedback in seconds without much additional waiting time. This can be as easy as calling python --version, which will fail with a non-zero return code if the binary is missing. More fine-grained assertions are possible, but should still remain fast.
If a certain binary should not be in the path, this can be asserted as well. The same goes for environment variables and file existence. Dedicated infrastructure testing tools, such as Serverspec could also be used, but having a response time under a minute is crucial in my view.
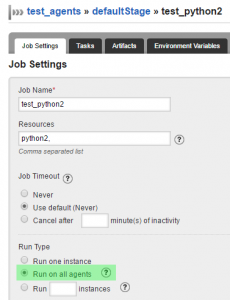
Run on All Agents
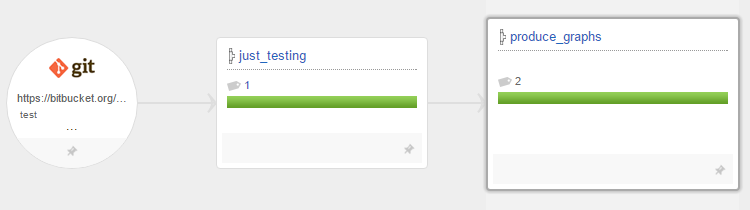
In order to validate the consistency of the CI infrastructure, the validation tasks should run on all agents that advertise a corresponding resource. This is where, in my view, the real power of GoCD comes to light, and the concepts used in it fit in the right places.
GoCD will run the test tasks on all agents that fulfill all resource requirements for the task.
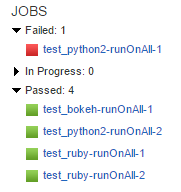
Test fails
Now that we have all the tests, running them gives quick and precise feedback:
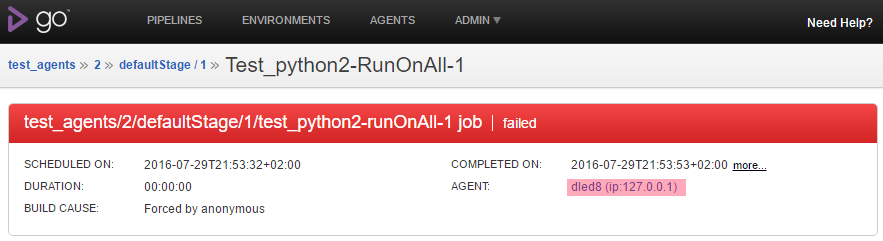
Checking out the job run details reveals the offending agent. Note the test duration: under 1 second.
Fixing the Infrastructure
Whatever the resolution of the infrastructure problem, when the infrastructure test has a good coverage of the prerequisites for a pipeline, adding new agents to the CI infrastructure should become as much fun as TDD is: write an infrastructure test, see it fail, fix the infrastructure, feel the good hormones. Add new build agents for speed — still works — great!
Note how the resources that are available only on one machine are only run on one corresponding machine.
Happy Pictures and Developers
When to Test
It is an open question, when to test the infrastructure. With the system being composed of the CI server and agents, the tests should probably run on any global state change, such as
- added/removed/reconfigured agents
- automatic OS updates (controversial)
- restarts
- network topology changes
It is also possible to schedule a regular environment check. Having the environment test pipeline be the input for other pipelines unfortunately will not do in the following sequence of events:
- environment tests pass
- faulty agents are added
- downstream pipeline is triggered
- environment failure causes a pipeline to fail
In any case, there is a REST API available for the GoCD server should automating the automation become a necessity.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank all the great minds, authors and developers who have worked and are working to make lives of developers and software users better. Tools and ideas that work and provide value are indispensable. The articles and the software linked in this blog entry are examples of knowledge that brings the software industry forward. I am also very grateful to my current employer for letting me learn, grow and make a positive impact.